The information in this article is not intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Instead, consult your physician or any licensed healthcare providers if you have medical questions to get personalized answers.
When you have high mean corpuscular volume or MCV in your blood test, it means your red blood cells (RBCs) are larger than normal and disrupt blood functions. This condition, known as macrocytosis, is often linked to underlying health issues and may warrant further investigation by your healthcare provider. They might suggest lifestyle adjustments, such as dietary changes and vitamin supplementation, alongside any necessary medications to address the root cause and help restore your MCV levels to a healthy range.
Find out more about what conditions cause high MCV and what it means for your health.
What Is MCV?
MCV, or mean corpuscular volume, is a blood test that measures the average size of your red blood cells. This value is obtained through a complete blood count (CBC) test, a standard blood test used to evaluate your overall health. It’s like a ruler for your red blood cells, telling you if they’re too big, too small, or just the right size. This information can help diagnose various health conditions, such as anemia, vitamin deficiencies, and liver disease.
MCV is often combined with other red blood cell tests, such as MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin), MCHC (mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration), and RDW (red blood cell distribution width). Together, these tests can give your doctor a complete picture of your red blood cell health and help pinpoint the underlying cause of any problems.
What Causes High MCV Levels in a Blood Test?
A high MCV blood test, where your mean corpuscular volume level is above 100 fl, is a key indicator of macrocytic anemia. Macrocytic anemia is a blood disorder characterized by abnormally large RBCs and can be linked to several health conditions, including intake of specific drugs. That said, having high MCV levels in blood tests can be due to the following reasons:
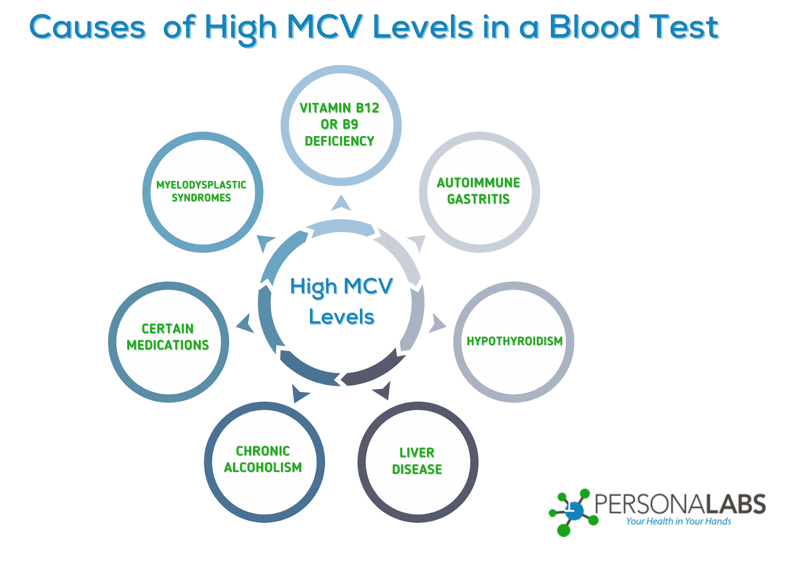
- Vitamin B12 or B9 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)(1) and vitamin B9 (folate)(2) are major players in RBC production, specifically in DNA synthesis, ensuring their proper formation and maturation. Lack of vitamin B12 and B9 causes deformities and size disparity in the RBCs. This can lead to abnormally large (macrocytic) red blood cells with irregular shapes, a condition often associated with a high MCV blood test.
If your MCV levels are high, your healthcare provider can help determine if a vitamin B12 or B9 deficiency(3) contributes to the elevated MCV and recommend appropriate steps. This may involve dietary adjustments to include more B12-rich foods like meat, fish, and dairy, and folate-rich foods like leafy green vegetables, legumes, and fortified cereals. In some cases, your doctor may advise vitamin B12 or B9 supplements to address the deficiency and support healthy red blood cell production.
Did You Know? Folate deficiency remains the most common cause of high MCV. Even the diseases associated with elevated MCV are linked to the malabsorption of vitamin B12 and B9. In that sense, you can avoid having high MCV in your blood test when you ensure the inclusion of the said vitamins in your diet.
- Autoimmune Gastritis
Elevated MCV can be observed in patients with autoimmune gastritis(4). It is a chronic condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the cells lining the stomach, particularly in the upper section known as the fundus and body. This attack leads to inflammation and damage, impairing the stomach’s ability to absorb vitamin B12.
As discussed above, a vitamin B12 deficiency results in larger-than-normal red blood cells, reflected in the elevated MCV blood test result. This type of anemia is often referred to as pernicious anemia(5).
While the exact cause of autoimmune gastritis remains unknown, genetic predisposition plays a significant role. Individuals with a family history of this condition are more likely to develop it.
Autoimmune gastritis can lead to serious complications, including an increased risk of stomach cancer if left untreated. Therefore, if you have an elevated MCV and experience symptoms like fatigue, weakness, or digestive issues, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for further evaluation and appropriate management.

Inflammation in the stomach impacts folate absorption, leading to high MCV.
- Hypothyroidism
Thyroid disorders can influence red blood cell production and size, potentially leading to an elevated MCV on a CBC. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in stimulating the production of red blood cells. However, it’s important to clarify that hypothyroidism(6), with its reduced thyroid hormone levels, typically leads to larger RBCs and, thus, a higher MCV. This occurs because the lack of thyroid hormone disrupts the normal maturation process of RBCs, resulting in fewer but larger cells.
Did You Know: Hypothyroidism leads to lower-than-normal thyroid hormones. This condition can be traced back to health issues, such as iron deficiency, thyroiditis, and problems with the pituitary gland.

Increased MCV levels are noted among individuals with hypothyroidism.
- Liver Disease
Liver disease can change the structure and composition of your RBCs. For example, if you have liver disease, you’re most likely to have increased cholesterol deposition in your RBCs(7), which leads to macrocytosis. Elevated phospholipids are linked to the impaired ability of the liver to regulate cholesterol.
In addition, elevated MCV levels also suggest the severity of liver damage, as shown in a study conducted among patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD(8). The researchers found that higher MCV values were associated with more advanced fibrosis stages, suggesting that MCV could be a potential marker for assessing the severity of NAFLD.
- Chronic Alcoholism
Chronic alcohol abuse(9) can significantly disrupt red blood cell production, potentially leading to an elevated MCV blood test result. Alcohol has a toxic effect on bone marrow, the primary site of red blood cell development. This can impair the marrow’s ability to produce healthy RBCs, resulting in a high MCV value. Additionally, alcohol can directly damage red blood cell membranes, altering their structure and further contributing to their increased size.
The good news is the damaging effects of alcohol on red blood cells are often reversible. With abstinence and appropriate support, the bone marrow can recover its function, leading to the production of normal-sized red blood cells and a gradual normalization of MCV levels. However, this is possible if the sole cause of high MCV levels is long-term alcoholism.

Overconsumption of alcohol can lead to elevated MCV levels.
- Certain Medications
Drugs that interrupt folate absorption(10) contribute to macrocytic anemia. Examples of such medications include methotrexate (used in chemotherapy), some antiretroviral drugs for HIV treatment, and certain antiseizure medications like phenytoin. These drugs can impede folate metabolism, hindering DNA synthesis within red blood cells and ultimately affecting their size and maturity.
If you are taking any of these medications and have concerns about high MCV levels in your blood work, it’s essential to consult your doctor. They can assess your situation, determine if the medication contributes to the elevated MCV, and recommend appropriate management strategies.
- Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)(11) are a group of cancers that disrupt the bone marrow’s ability to produce healthy blood cells. Instead of developing normally, the blood cells produced are often faulty, immature, and don’t function properly. This can lead to a shortage of healthy red blood cells, white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets, causing symptoms like fatigue, infections, and easy bruising.
One common finding in MDS is high MCV levels(12). The dysfunctional bone marrow in MDS can impair the process of red blood cell division and maturation, resulting in abnormally larger RBCs circulating in the bloodstream. This abnormal MCV value, along with other blood test abnormalities, can be a clue in diagnosing MDS.
How an MCV Blood Test Works
MCV is a key measurement in hematology, providing valuable insights into red blood cell health. Analyzing MCV values aids healthcare professionals in diagnosing various conditions, particularly anemias, and guiding appropriate treatment strategies. Understanding how this test works illuminates its significance in patient care.
The MCV lab test goes hand-in-hand with other tests that determine the characteristics of RBC, such as the following:
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) measures the average amount of hemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen) in the RBC.
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) screens for the concentration level of hemoglobin in an RBC.
- Red cell distribution width (RDW) compares the sizes of RBCs and determines significant differences.
Analyzing these indices allows doctors to diagnose different types of anemia and other health conditions that affect hemoglobin production and red blood cell size. For instance, a low MCV and MCHC often signal iron deficiency anemia, while a high MCV might suggest a vitamin B12 or folate deficiency. Furthermore, examining these indices in conjunction with other clinical data provides a more comprehensive understanding of a patient’s overall health.
How Is the Test Done?
An MCV lab test requires a blood sample drawn from the veins. That’s why it has to be performed in a trusted laboratory. No special preparation is necessary, especially if it’s part of a CBC test. However, your doctor may request that you fast for 8 hours, depending on the purpose of the test.
A blood sample extracted through venipuncture is needed for an MCV lab test.
Pro tip: An MCV blood test involves venipuncture, which can be a panic-filled experience for some. If you’re anxious about having a needle inserted in your veins, perhaps you can ease up the anxiety by knowing how to prepare for blood extraction. Check out our expert tips for getting blood drawn for a lab test.
MCV Blood Test Range
The normal MCV blood test range is from 80 to 100 femtoliters (fl). If your test results indicate above the upper limit of the range (>100 fl), your RBCs may be larger than normal, suggesting macrocytic anemia. On the other hand, if it is below 80 fl or the lower limit, you’re likely to have microcytic anemia.
When Should You Take the MCV Blood Test?
Doctors often recommend the MCV blood test when symptoms of anemia, specifically macrocytic and microcytic anemia (RBCs are smaller than the average size), appear. These symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- Numbness and tingling in the extremities
- Trouble concentrating
- Appetite loss
- Irritability
Your doctor may also order this blood test as part of your wellness checkup. But often, it’s a response to verify symptoms of the conditions mentioned above.
Treatment for High MCV
Addressing a high MCV level effectively hinges on identifying its root cause. Since an elevated MCV can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, your doctor will conduct a thorough evaluation to pinpoint the specific factor contributing to the larger-than-normal red blood cells. This may include reviewing your medical history, performing a physical examination, and ordering additional tests, such as vitamin B12 and folate level checks, liver function tests, and thyroid hormone assessments.
Once the underlying cause is determined, your doctor will develop a targeted treatment plan. It could involve addressing nutritional deficiencies through dietary changes or supplements, managing chronic conditions like hypothyroidism or liver disease with appropriate medications, or treating alcohol abuse.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does high MCV mean cancer?
High MCV levels in a blood test do not automatically mean cancer. Macrocytosis, reflected by elevated MCV, is linked to different disorders, which include cancer. Hence, if you have elevated MCV, you’ll likely have to take other lab tests to diagnose the cause of the condition properly.
What cancers cause high MCV levels?
Liver cancer is the most associated type of cancer with high MCV levels since liver dysfunctions lead to more fats adhering to the membrane of the red blood cells. This, in turn, increases their surface levels. Other cancers, such as colorectal and esophageal cancers, could also lead to macrocytic anemia.
What does high MCV and MCH mean?
If your MCV and MCH levels are high, it clearly shows macrocytic anemia. MCH measures the average concentration of hemoglobin in the red blood cells. High MCH correlates with the large size of the RBC, as measured by the MCV blood test. You’re likely to have elevated MCV and MCH if you have folate deficiency, thyroid problems, and liver disease.
How should I lower my MCV levels?
Lowering your MCV levels requires better understanding and/or diagnosing the cause of the macrocytosis. But on top of medical treatment, you can help normalize high MCV by adjusting your diet accordingly, supplementing your vitamin intake, and regulating your alcohol intake.
How Long Does It Take for MCV To Return to Normal?
When the proper treatment is set, you can expect to have your high MCV levels fixed within 2 to 4 months. For example, if you withdraw from alcohol consumption and increase your dietary intake of folate-rich foods, your bone marrow will produce normal-sized RBCs, provided that there are no other factors for the condition.
The Bottom Line
The CBC test provides information about your blood, including your red blood cell structure and count. As it often includes the MCV test, it’s best to understand the results and what it means for your health to have high MCV levels. For a more personalized assessment and treatment, we recommend consulting your doctor promptly.
Sources
1 Al Amin ASM, Gupta V. Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) [Updated 2023 Jul 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559132/
2 Merrell BJ, McMurry JP. Folic Acid. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554487/
3 Maner BS, Killeen RB, Moosavi L. Mean Corpuscular Volume. [Updated 2024 Jul 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545275/
4 Singh S, Chakole S, Agrawal S, Shetty N, Prasad R, Lohakare T, Wanjari M, Yelne S. A Comprehensive Review of Upper Gastrointestinal Symptom Management in Autoimmune Gastritis: Current Insights and Future Directions. Cureus. 2023 Aug 13;15(8):e43418. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43418. PMID: 37706145; PMCID: PMC10496934.
5 Cotton M, McCaddon A. Examining the Diagnosis and Treatment Experiences of People Living With Autoimmune Gastritis and Pernicious Anemia. J Patient Exp. 2023 Jan 17;10:23743735231151767. doi: 10.1177/23743735231151767. PMID: 36698620; PMCID: PMC9869222.
6 Wang M, Lu X, Zheng X, Zhu X, Liu J. Associations among thyroid hormone levels and mean corpuscular volume in adults in the US: A cross-sectional examination of the NHANES 2007-2012 dataset. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 8;103(10):e37350. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037350. PMID: 38457537; PMCID: PMC10919465.
7 Allameh A, Niayesh-Mehr R, Aliarab A, Sebastiani G, Pantopoulos K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 22;12(9):1653. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091653. PMID: 37759956; PMCID: PMC10525124.
8 Zhu N, Wang X, Zhu H, Zheng Y. Blood cell parameters and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a comprehensive Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Apr 23;17(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01879-7. PMID: 38654378; PMCID: PMC11040836.
9 Pohjasniemi, Heidi & Hietala, Johanna & Anttila, Petra & Parkkila, Seppo & Niemelä, Onni. (2006). Long-term ethanol consumption and macrocytosis: Diagnostic and pathogenic implications. The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine. 147. 191-6. 10.1016/j.lab.2005.12.004.
10 Khan KM, Jialal I. Folic Acid Deficiency. [Updated 2023 Jun 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535377/
11 Karel D, Valburg C, Woddor N, Nava VE, Aggarwal A. Myelodysplastic Neoplasms (MDS): The Current and Future Treatment Landscape. Curr Oncol. 2024 Apr 3;31(4):1971-1993. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31040148. PMID: 38668051; PMCID: PMC11049094.
12 Urrechaga E, Fernández M, Aguirre U. Complete Blood Counts and Research Parameters in the Detection of Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 21;14(13):1322. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131322. PMID: 39001213; PMCID: PMC11240308.

